Peptide dosage calculator
Unsure how many units of Semaglutide/Tirzepatide/Retatrutide to take? No worries, we made a calculator for you
Got any questions?
Contact us!
Peptide Calculator
Choose Peptide Dosage:
Standard recommended dosages
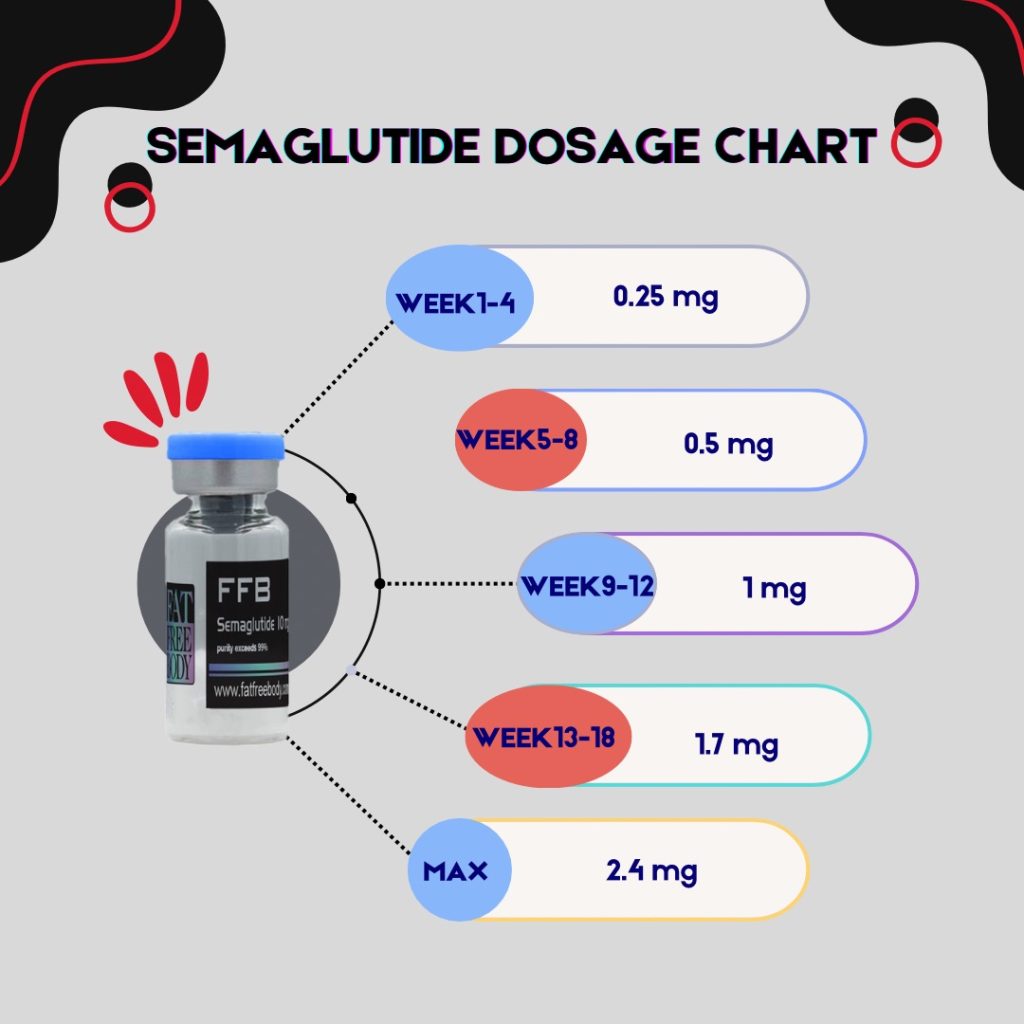
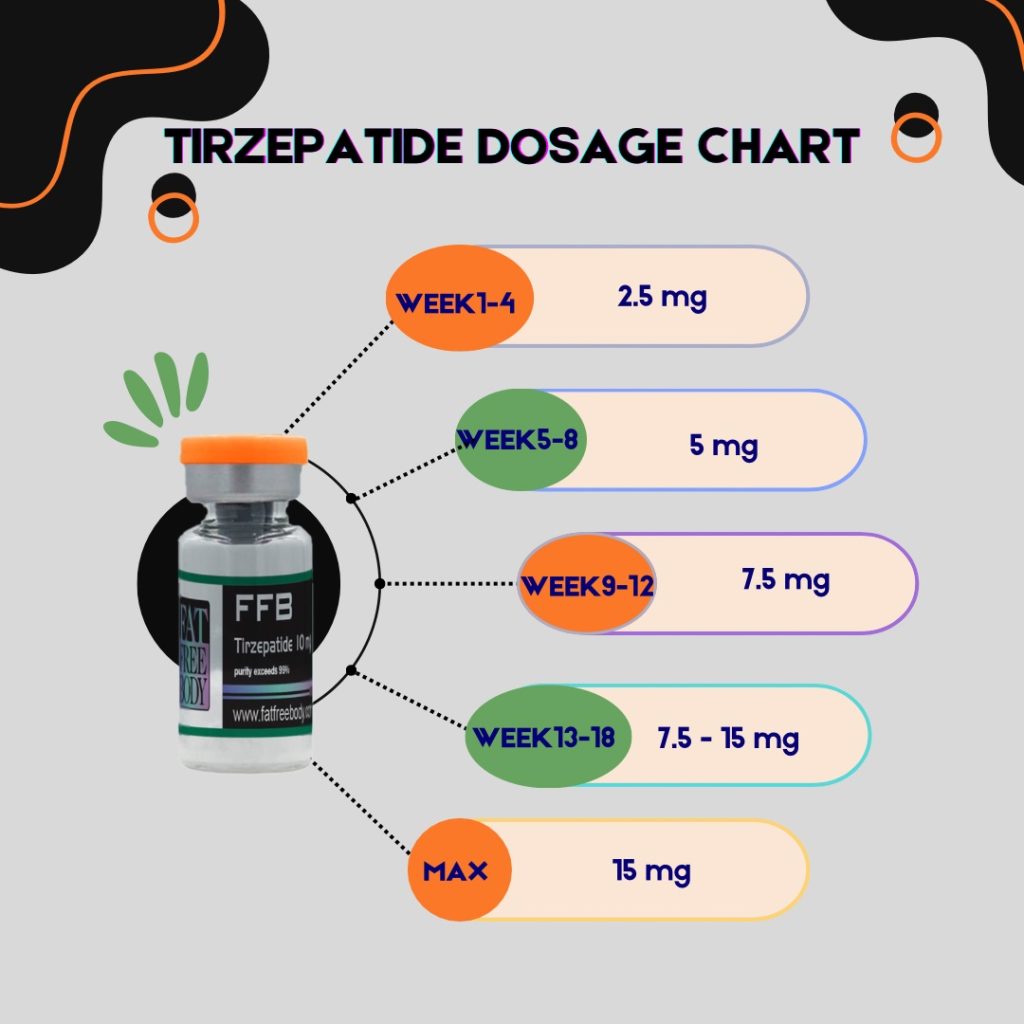
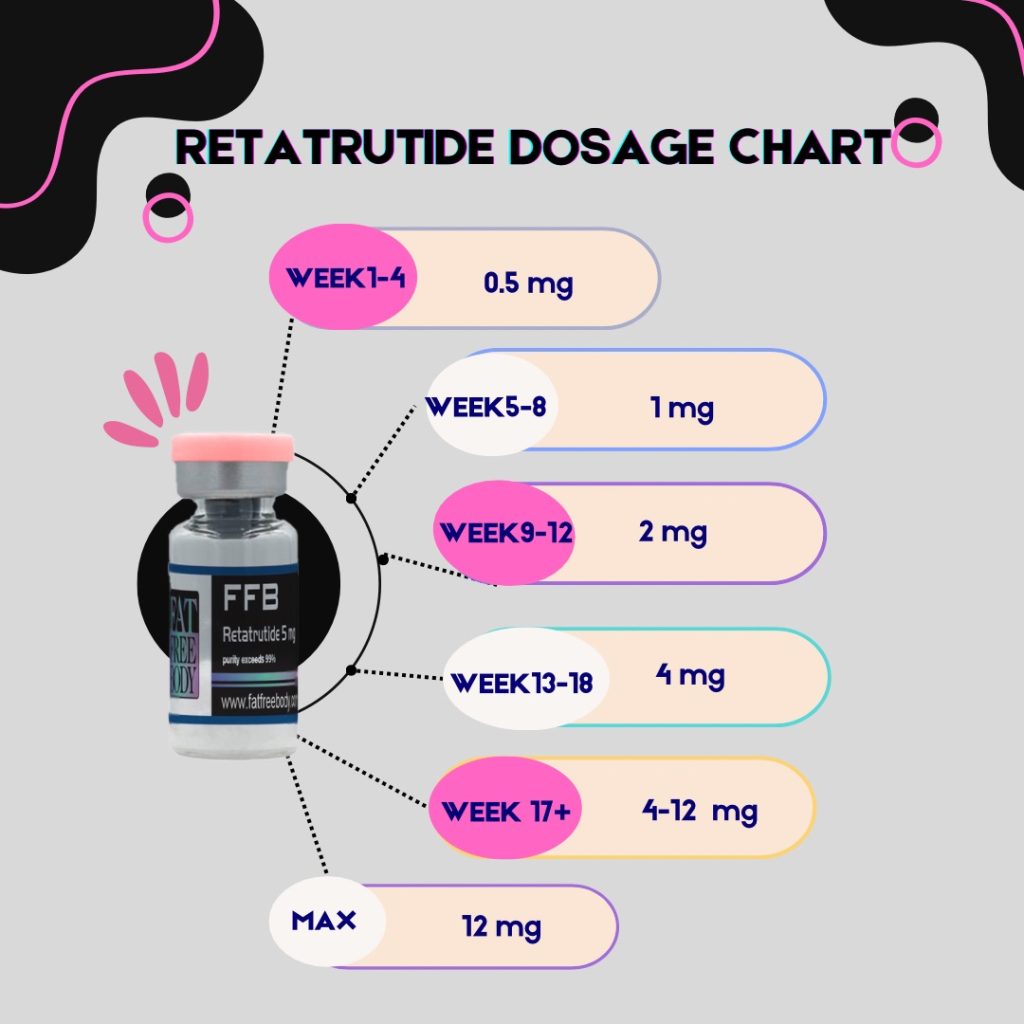
These are the most commonly recommended dosage escalations for Semaglutide, Tirzepatide and Retatrutide. It’s not recommended to exceed the max dosage without consulting with your GP or other medical professionals.
High quality weight loss peptides, domestic shipping
How to Calculate Dosage When Reconstituting Weight Loss Peptides Like Semaglutide, Tirzepatide, and Retatrutide
Reconstituting peptides correctly and calculating the precise dosage is essential to ensure that you receive the intended benefits of your treatment. Follow the steps below to accurately calculate your dosage and administer it safely
Step 1: Understand Your Peptide Vial’s Concentration
Each peptide vial will have a specific concentration, usually indicated on the vial (e.g., 5mg, 10mg, 15mg). This tells you how much peptide powder is in the vial.
- Tip: Write down the concentration (e.g., 10mg) so you have it ready for calculations in later steps.
Step 2: Add the Correct Amount of bacteriostatic or Sterile Water
Bacteriostatic water is used to reconstitute the peptide powder into a liquid for injection.
Decide how much water you will add: Common options are 1ml, 2ml, 3ml, or 5ml of bacteriostatic water.
- 1ml = 100 units
- 2ml = 200 units
- 3ml = 300 units
- 5ml = 500 units
Inject the water into the vial:
- Insert the needle into the vial of peptide powder, and slowly inject the bacteriostatic water along the inner wall of the vial to avoid bubbling or damaging the peptide.
Let it dissolve: After adding the water, gently swirl (but do not shake) the vial until the peptide powder fully dissolves.
- Tip: Ensure the amount of water you use matches your planned dosage calculations. More water results in a more diluted solution, but also finer control over smaller doses.
Step 3: Calculate the Dosage Per Unit
Once the peptide powder has dissolved in the bacteriostatic water, you can calculate the amount of peptide in each unit on your syringe.
Formula:
Peptide Concentration (mg) / Total Units (based on water added)
Example Calculation:
- Peptide Amount: 10 mg in the vial
- Water Added: 2 ml (which corresponds to 200 units)
Total Units Calculation:
2 ml = 200 units
Peptide Concentration Calculation:
10 mg / 200 units = 0.05 mg (50 mcg) per unit
Tip: Write down this number as it will be used to determine your actual dosage.
Step 4: Determine Your Required Dosage
Now that you know how many milligrams (or micrograms) are in each unit, determine how much peptide you need to inject for your required dose.
For example, if your dosage is 0.5 mg (0.500 mcg) and your calculation shows 0.05 mg per unit, then:
Divide the required dose by the mg per unit:
0.5 mg / 0.05 mg = 10 units
This means you would need to draw 10 units of the peptide solution into the syringe.
Step 5: Use the Correct Syringe
Most peptides are injected using insulin syringes, which come in different sizes: 0.3ml (30 units), 0.5ml (50 units), or 1ml (100 units).
- Tip: Make sure to use the correct syringe size for your calculations. If you need more control over smaller doses, you can use a 0.3ml (30-unit syringe) for better accuracy with lower doses.
Step 6: Administer the Dose
Now that you’ve calculated the correct dosage:
Draw the correct amount of the reconstituted peptide solution into the syringe (e.g., 10 units).
Inject subcutaneously (into the fatty tissue, usually around the abdomen).
- Pinch a fold of skin, insert the needle at a 45-degree angle, and slowly push the plunger to inject the peptide.
Dispose of the syringe safely after use.
Example Dosage Calculations
Example 1:
Peptide vial: 5 mg
Water added: 1 ml (100 units)
Desired dose: 1 mg
Calculation:
mg per unit:
5 mg / 100 units = 0.05 mg per unit
Units needed for 1 mg dose:
1 mg / 0.05 mg per unit = 20 units
You would need to draw 20 units of the solution for a 1 mg dose.
Example 2:
Peptide vial: 10 mg
Water added: 2 ml (200 units)
Desired dose: 0.5 mg (500 mcg)
Calculation:
mg per unit:
10 mg / 200 units = 0.05 mg per unit
Units needed for 0.5 mg dose:
0.5 mg / 0.05 mg = 10 units
You would need to draw 10 units for a 0.5 mg dose.
Final Tips:
- Double-check your math: Before administering any dose, make sure you’ve calculated everything correctly.
- Start with a lower dose: If you’re new to peptide treatments, it’s often a good idea to start with a lower dose to see how your body reacts.
- Use a clean, sterile environment: Always make sure you’re working in a clean area and using sterile equipment to avoid contamination.